
rotation of earth (lesson 0291) TQA explorer
Geometrical optics, or ray optics, is a model of optics that describes light propagation in terms of rays.The ray in geometrical optics is an abstraction useful for approximating the paths along which light propagates under certain circumstances.. The simplifying assumptions of geometrical optics include that light rays: propagate in straight-line paths as they travel in a homogeneous medium
Geography Rays sunlight Download free picture №212831
The Basics of Waves. Figure 5.1.1 5.1. 1: Amplitude and Wavelength. In the figure above, λ λ is the wavelength in meters and A A is the amplitude in μm − cm μ m − c m. If you were to stand at x 1 and watch the wave go by, you would see Figure 5.1.1 5.1. 1: where T is the period in s and f f is the frequency in Hz.
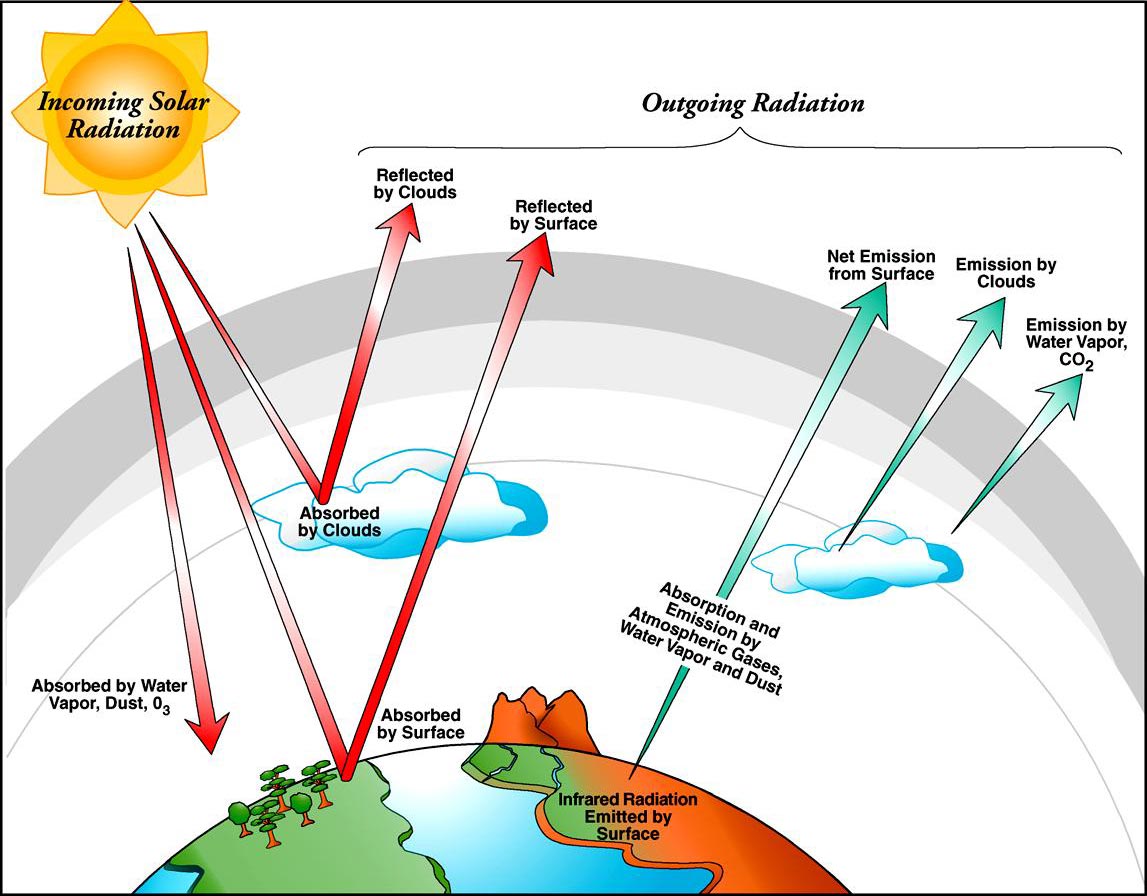
Science Made Simple What is Atmospheric Radiation?
A ray is defined as an end point followed by a sequence of points extending infinitely in one direction. The end point can also be thought of as the point of origin for the ray. The ray's length.

The Earth Climate Zones Depending on Angle of Sun Rays and Major
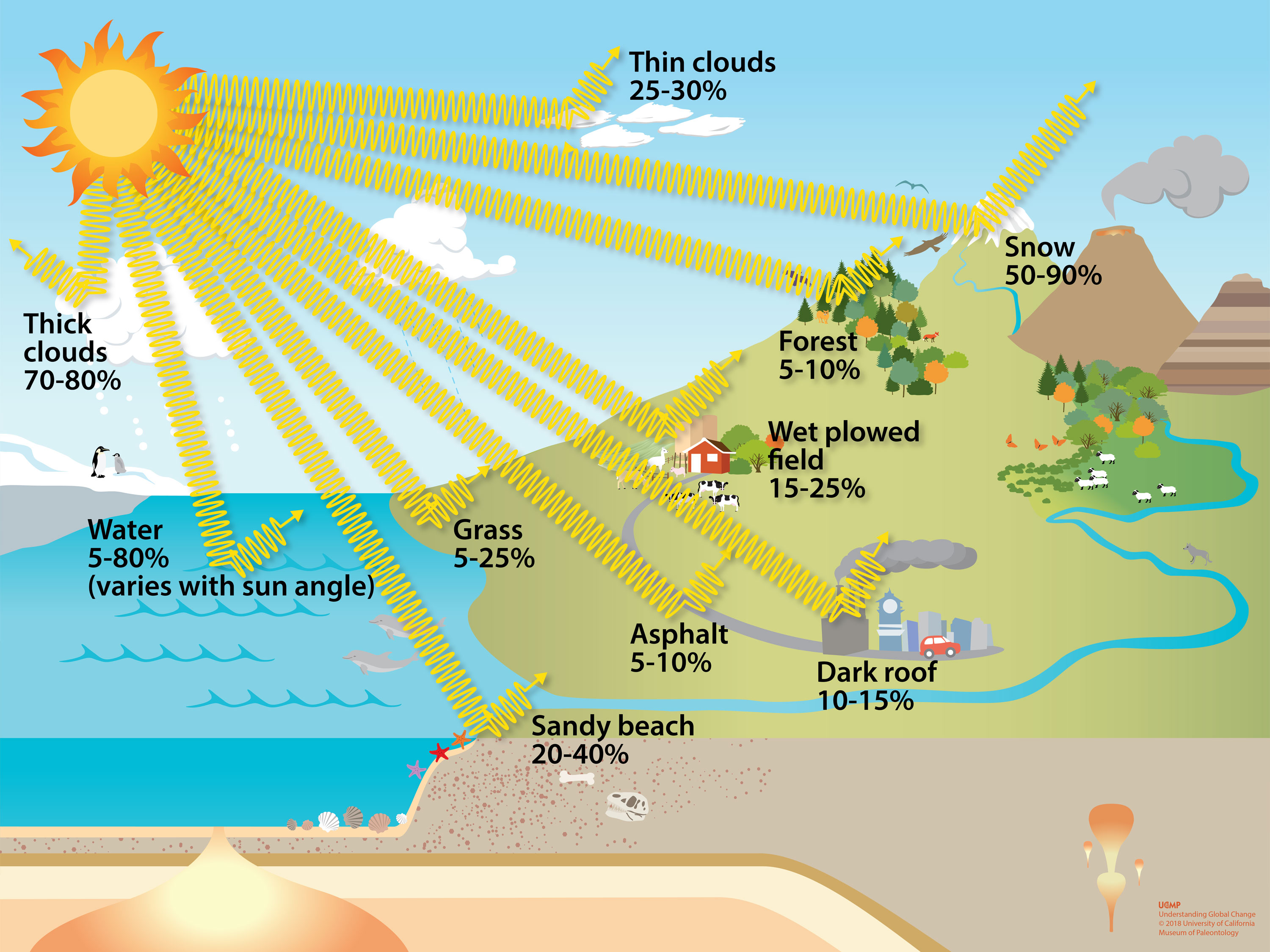
When the angle of incidence is at a 90° angle to the Earth (called direct or perpendicular rays), approximately 75% of the radiation emitted from the Sun reaches the surface of the Earth. Throughout the year, the angle of the Sun's rays are low (less than 25°) at the poles, compared to those closer to the equator.

A pelagic manta ray Photo by Tatiana Gonnason — National Geographic
Scale is the relationship of distance in the map versus the distance in the real world. A 1:1000 scale map, for example, would mean that 1 meter on the map equals 1000 meters, or 1 kilometer, on Earth's surface. Scale can sometimes be a confusing concept, so it's important to remember that it refers to a ratio.

solstice Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
AboutTranscript. A ray is a shape that starts at one point and extends forever in one direction. To identify a ray in a picture, look for a line that has one endpoint (the point where the ray starts) and an arrow on the other end (to show that it keeps going).
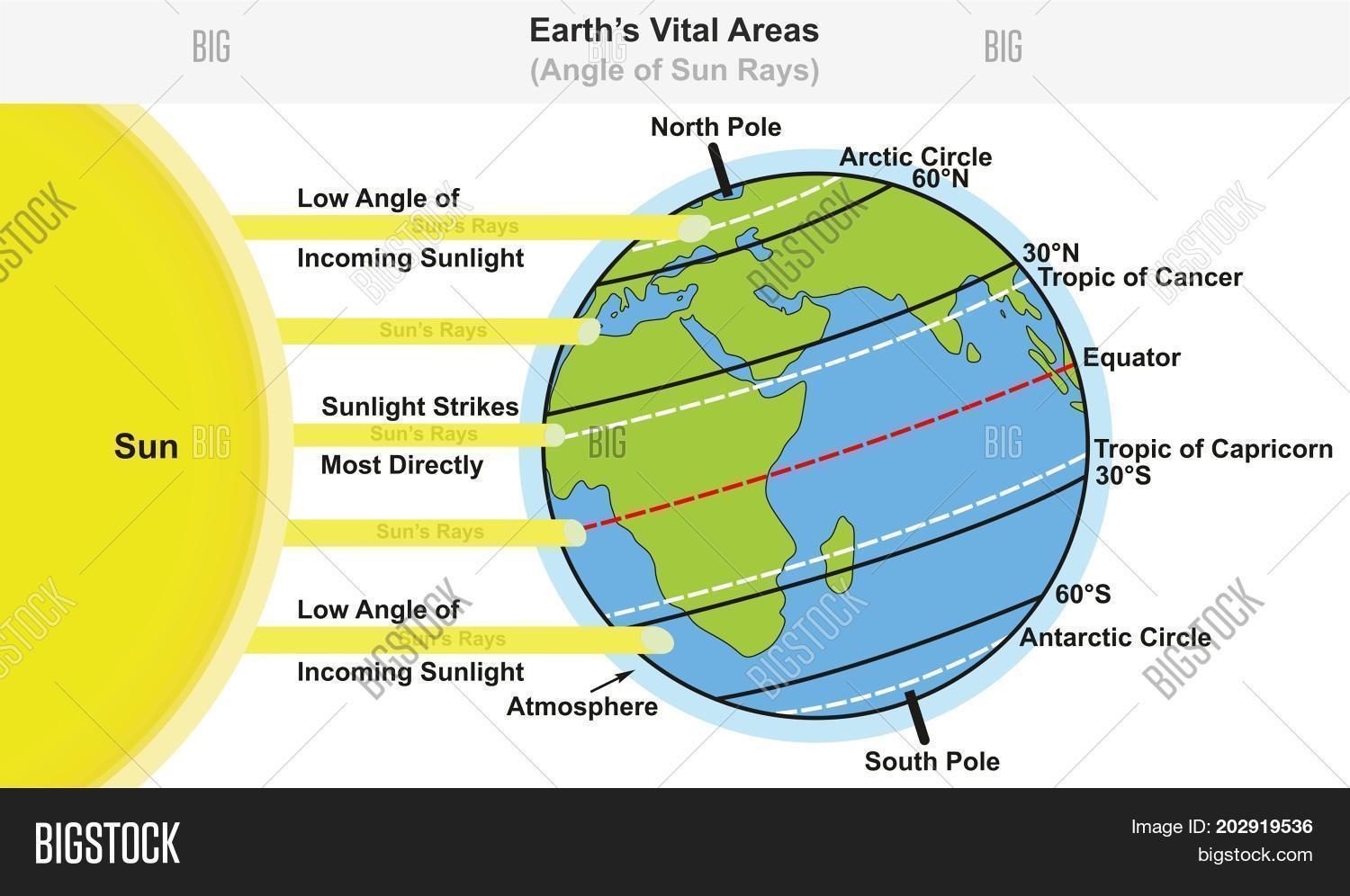
Earthâ s Vital Image & Photo (Free Trial) Bigstock
Geography is about spatial understanding, which requires an accurate grid system to determine absolute and relative location. Absolute location is the exact x- and y- coordinates on the Earth. Relative location is the location of something relative to other entities. For example, when you use Google Maps, you put in an absolute location.
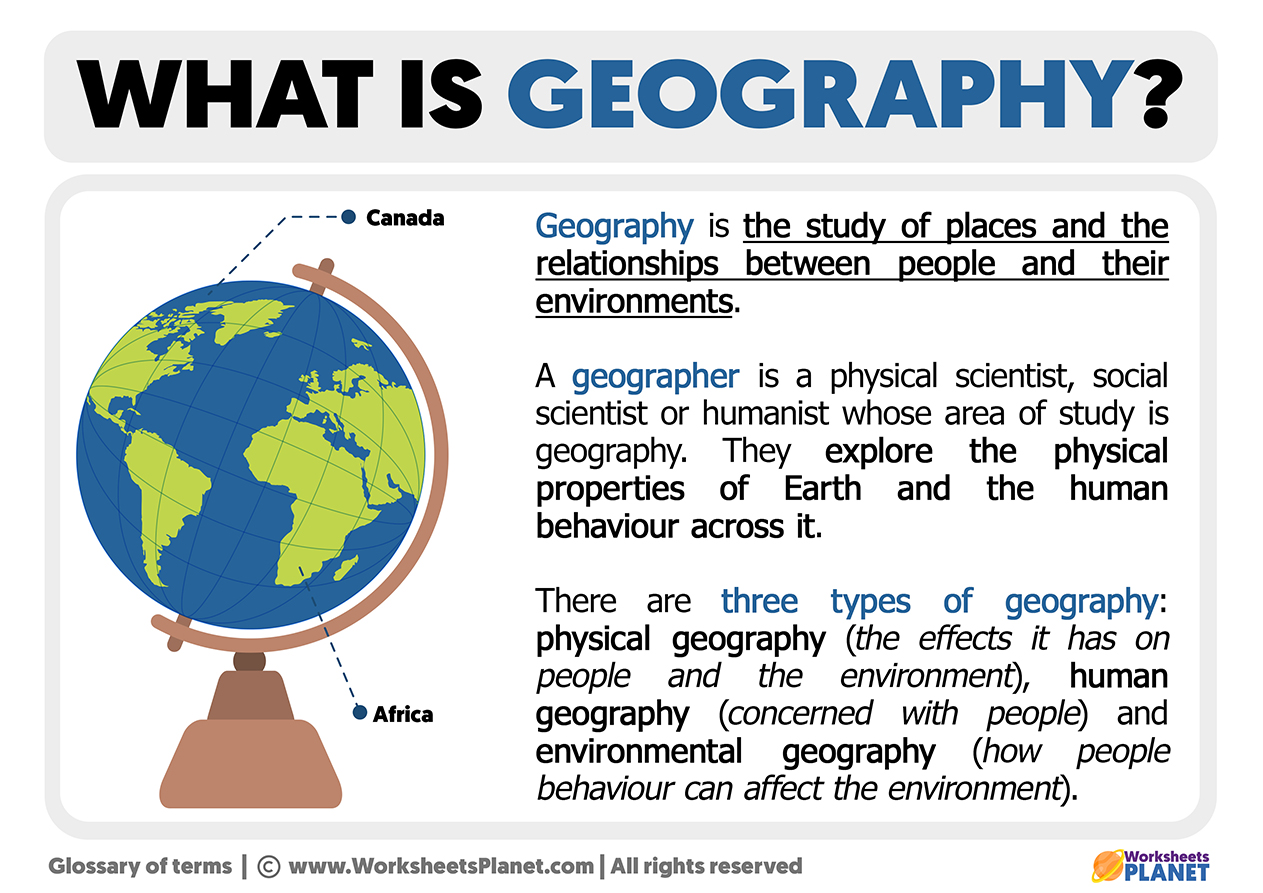
What is Geography Definition of Geography
geography, the study of the diverse environments, places, and spaces of Earth's surface and their interactions. It seeks to answer the questions of why things are as they are, where they are. The modern academic discipline of geography is rooted in ancient practice, concerned with the characteristics of places, in particular their natural environments and peoples, as well as the relations.

Ray history and some interesting facts
Step 2. Place a blank piece of paper along the transect line (index cards work great). Make sure you align the left corner to the end of the transect you drew. Step 3. Make a small mark where the index card intersects the contour line on the map and the index card, as seen in Figure 2.10.
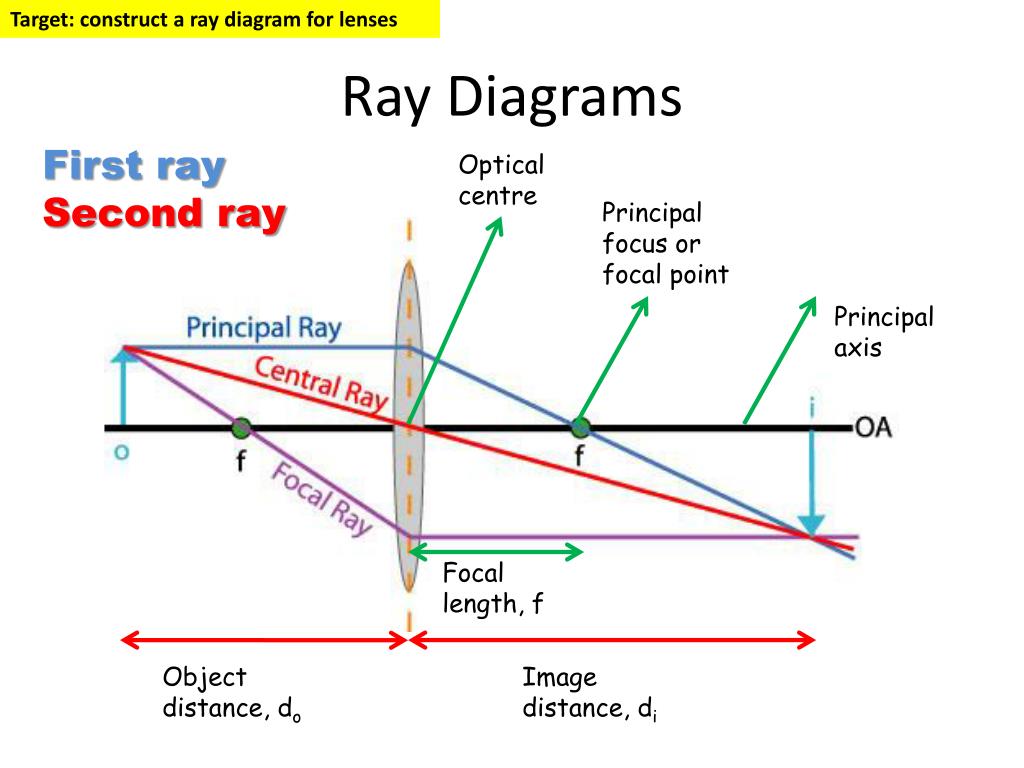
PPT Ray Diagrams PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6878954
How cosmic rays helped find a tunnel in Egypt's Great Pyramid. A man rides a donkey through the desert near the Great Pyramids of Giza. Modern technology is enabling scientists to peer inside.
Photovoltaic System Solar Energy
In the realm of geometry, a ray holds a significant position as one of the fundamental elements used to describe lines and angles. It is a concept that allows us to extend the notion of a line segment infinitely in one direction. To grasp the essence of a ray, let's delve into its definition and key characteristics.

Energy from the Sun Physical Geography
The definition of ray in math is that it is a part of a line that has a fixed starting point but no endpoint. It can extend infinitely in one direction. Since a ray has no end point, we can't measure its length. Fun Facts: The sun rays are an example of a ray. The sun is the starting point or the point of origin, and its rays of light extend.

Earth's Field Facts (All You Need to Know!)
A solstice is an event in which a planet 's poles are most extremely inclined toward or away from the star it orbits. On our planet, solstices are defined by solar declination —the latitude of Earth where the sun is directly overhead at noon. On Earth, solstices are twice-yearly phenomena in which solar declination reaches the Tropic of.
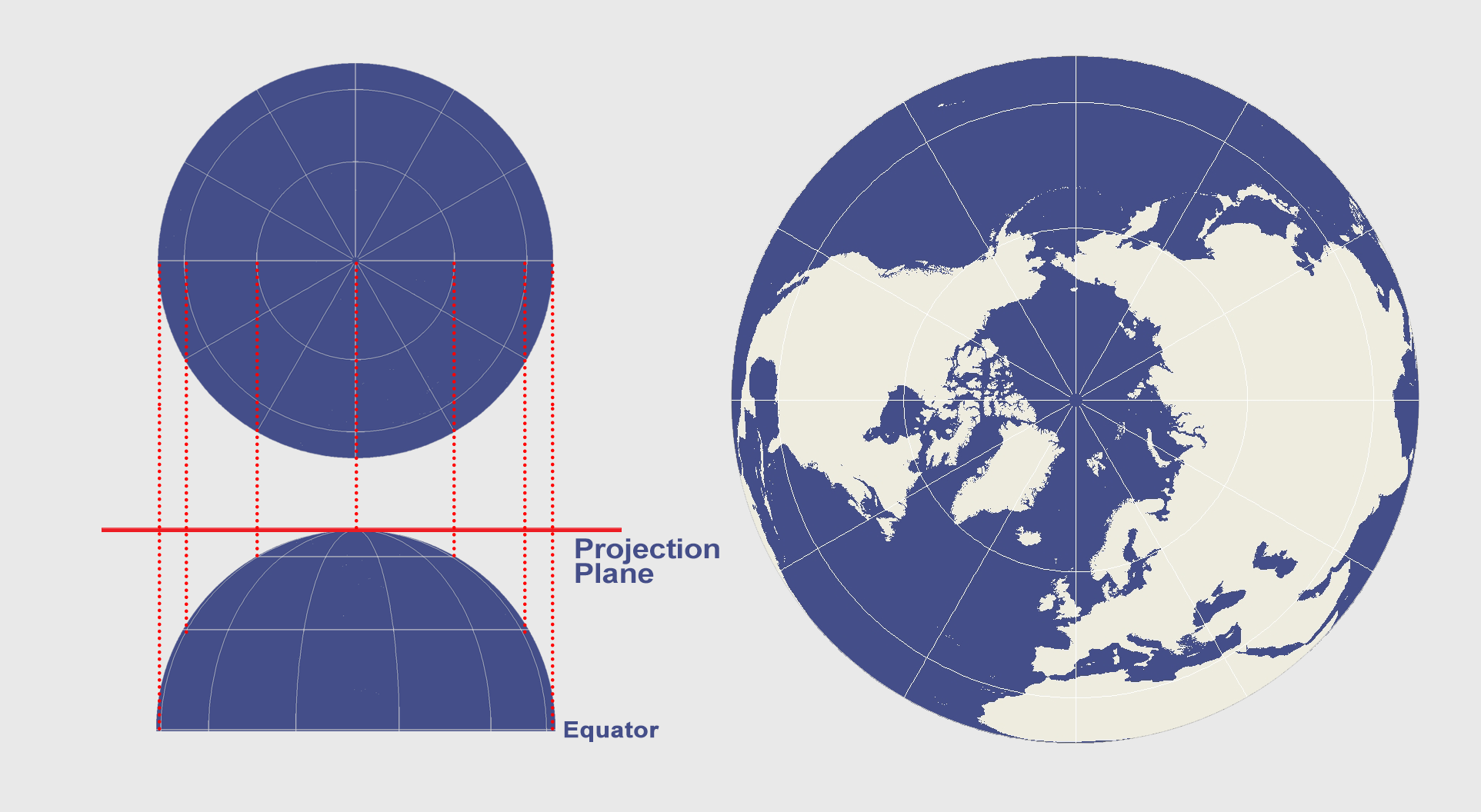
Azimuthal Projection Orthographic, Stereographic and Gnomonic GIS
Geography is an interdisciplinary discipline with a lot of commonalities with other disciplines. It also bridges both the natural and social sciences as a way of producing a more holistic understanding. Geographers tend to focus on places, locations on Earth distinguished by cultural and physical characteristics.

Trending Slanting rays of sun on frigid zone
A school of spotted eagle rays glides gracefully through the island-speckled waters of the Maldives. The rays are often seen gathering in groups near the surface, "flying" through the water by.

Cosmic ray air shower. The primary cosmic ray is a highenergy particle
A ray is a fundamental geometric figure that consists of a part of a line with a fixed starting point, known as the endpoint, and extends infinitely in one direction. It can be visualized as an arrow pointing towards infinity. Rays are essential building blocks for constructing angles and understanding the relationship between lines and points.