
Circle Theorems Poster Math poster, Circle theorems, Math charts
Circle theorems are used in geometric proofs and to calculate angles. Part of Maths Geometry and measure Angles at the centre and circumference - Higher The angle subtended by an arc at the.

GCSE circle theorem revision cards Circle theorems, Gcse math, Gcse maths revision
The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Circle Theorems. Corbettmaths Videos, worksheets, 5-a-day and much more. Menu Skip to. Primary; 5-a-day. 5-a-day GCSE 9-1; 5-a-day Primary; 5-a-day Further Maths; More. Further Maths; GCSE Revision; Revision Cards; Books; April 4, 2018 October 31, 2023 corbettmaths. Circle Theorems Practice Questions.

Circle theorems GCSE Maths revision Exam paper practice & help YouTube
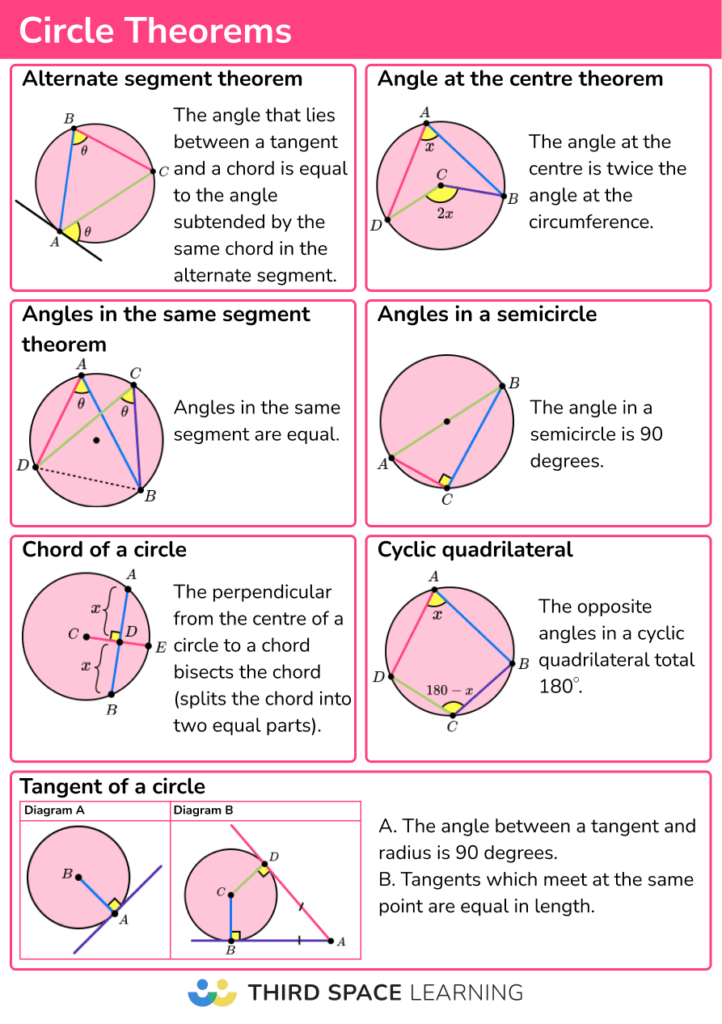
Theorem by Theorem Angles in the same segment are equal. The angle in a semicircle is a right angle The tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius. Two tangents to a circle from a point are equal. The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference.

Circle Theorems Notes Corbettmaths
GCSE AQA Circle theorems - Higher - AQA Chords - Higher Circles have different angle properties described by different circle theorems. Circle theorems are used in geometric proofs.
Circle Theorems Part 1 (of 4) Teaching Resources
You should be familiar with all 8 circle theorems to the point where: a) You can identify when they should be used. b) You can describe which one you've used with appropriate language. Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing Circles Interior and exterior angles Basic geometry rules

Identifying Circle Theorems Powerpoint (Higher GCSE) Teaching Resources
The theorem states that a tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency. In simpler terms, the angle formed between a tangent line and a radius at the point where the tangent meets the circle is always a right angle (90 degrees).

Circle Theorems GCSE maths question 1 YouTube
Circle theorems are properties that show relationships between angles within the geometry of a circle. We can use these theorems along with prior knowledge of other angle properties to calculate missing angles, without the use of a protractor. This has very useful applications within design and engineering. There are seven main circle theorems:

Circle Theorems Gcse Worksheet
C D A, B and C are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O. DCE is a tangent to the circle. Angle ABC = 61° Angle ACB = 73° Angle BCE = x° Find the value of x. Give reasons for each stage of your working. (Total for Question 11 is 3 marks) A O 65° D C E

SOLUTION Circle theorems gcse worksheet grade 5 Studypool
Maths revision video and notes on the topic of Circle Theorems.

Circle Theorems powerpoint lesson. GCSE Foundation Maths. Teaching Resources
Download PDF Test Yourself Circle Theorem Proofs The circle theorems can be proved using knowledge of basic angle facts and properties of 2D shapes. If you are asked to prove a circle theorem, adding in any radii and finding all equal angles will help. There are two types of proofs that can be used for the different circle theorems.

Circle theorems poster Math examples, Circle theorems, Gcse past papers
. There are seven circle theorems. An important word that is used in circle theorems is . Subtending An angle is created by two chords . The angle in between the two chords is subtended by.

Circle Theorems Maths Charts Gloss Paper measuring 594 mm x 850 mm (A1) Math Charts for
A video revising the techniques and strategies for learning each of the circle theorems (Higher Only).This video is part of the Geometry module for Circle Th.

Circle Theorems Poster Teaching Resources
Specification notes. G10. Apply and prove the standard circle theorems concerning angles, radii, tangents and chords and use them to prove related results. including. angle at centre is equal to twice angle at circumference; angle in a semi-circle is 90°; angles in the same segment are equal; opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral sum to 180°;
Circle Theorems GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet
Theorem 5. In a cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles add up to 180°. In the above diagram, It is important to note that to make a the circumference of the circle. xx +yy =180°. cyclic quadrilateral, all vertices should be touching. Example: In the following diagram, find the value of and Diagram not drawn to scale.

Gcse Maths Circle Theorems Worksheet
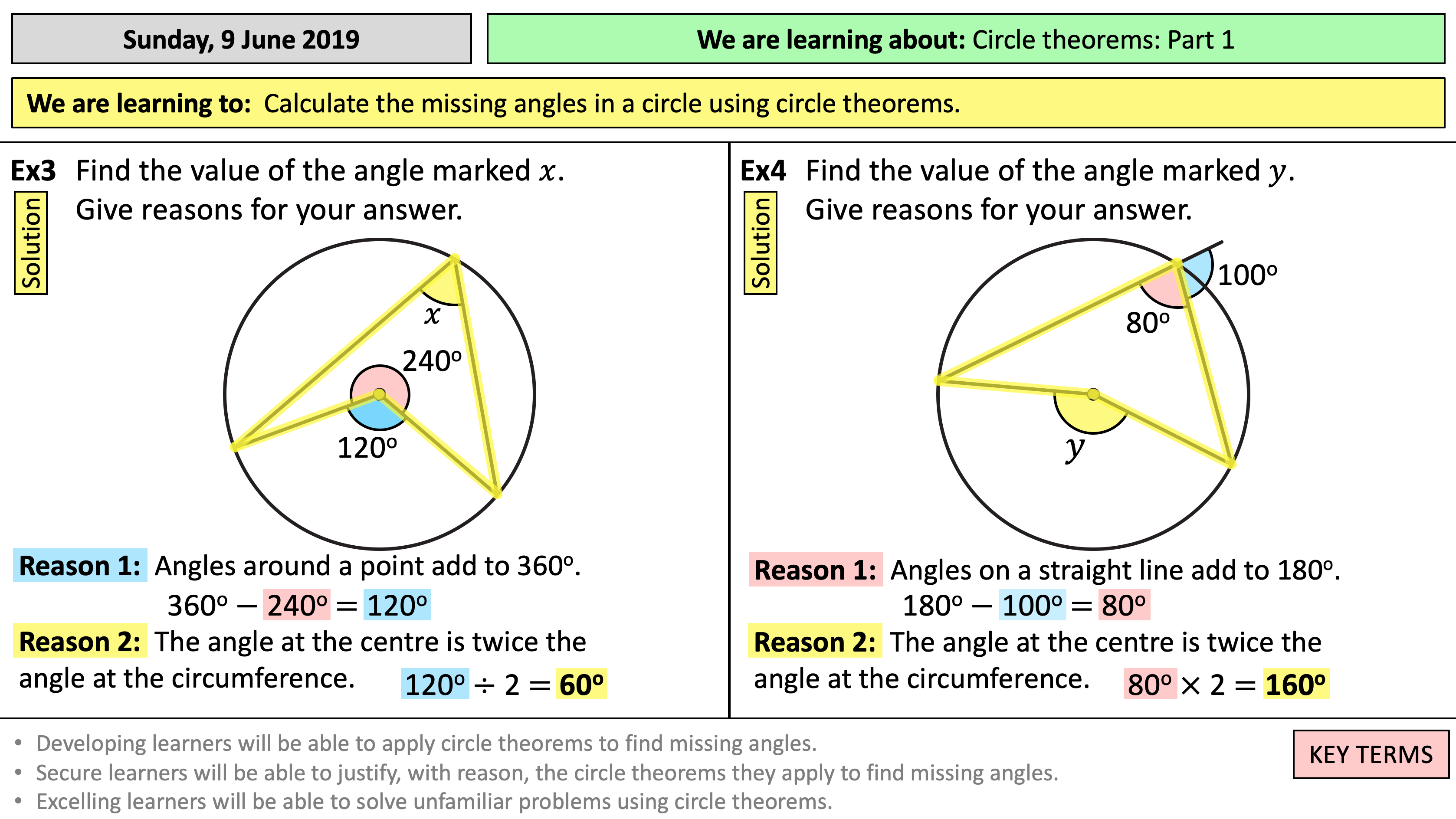
STEP 1 Find any two radii in the circle and follow them to the circumference STEP 2 See if there are lines from those points going to any other point on the circumference If you are asked for a reason in an exam and you use this theorem, use the key phrase; "The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference "

GCSE Maths Circle Theorems A2 Poster Tiger Moon
Practice questions can be found here: https://mathskitchen.com/?utm_source=YouTube&utm_medium=descriptionlink&utm_campaign=circletheoremfullCircle theorems q.