
Chemical Reactions Involved in Baking a Cake Sciencing
The process of bread baking is indeed a chemical reaction as it involves the transformation of ingredients into a completely different product through a series of chemical processes. The science behind bread baking is not only fascinating but also plays a crucial role in the art of creating delicious, fresh bread.
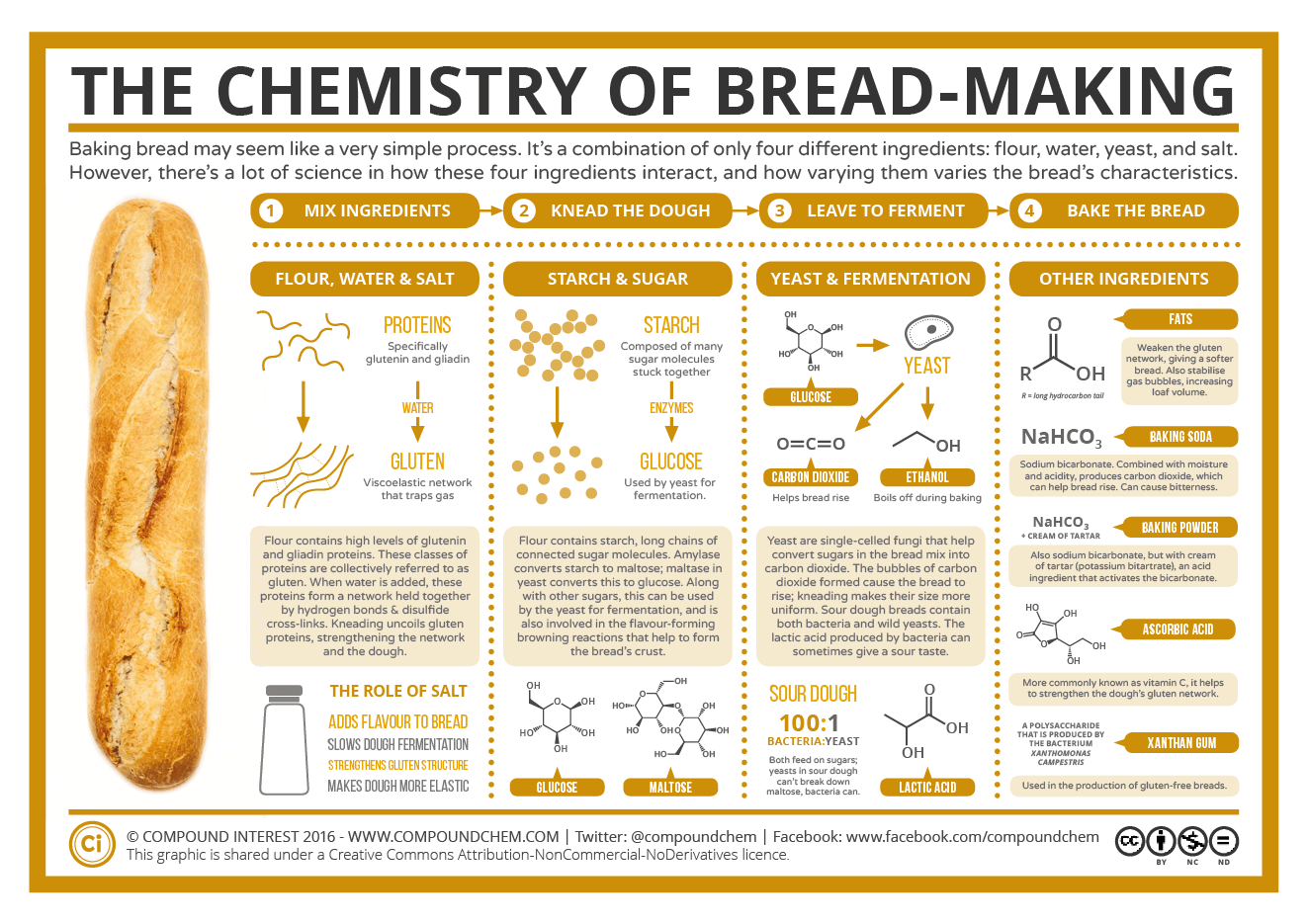
Baking Bread The Chemistry of BreadMaking Compound Interest
The answer is yes, it involves a chemical change. When the dough is placed in the oven, the heat causes the yeast to produce carbon dioxide gas, which makes the dough rise. This process, known as fermentation, is a chemical change that results in the formation of new substances. In addition, the heat causes the proteins and starches in the.

Chemical Equation for Baking Soda and Vinegar Reaction
Baking powder or baking soda work quickly, relying on chemical reactions between acidic and alkaline compounds to produce the carbon dioxide necessary to inflate dough or batter (more on this later). Baking powder and baking soda are used to leaven baked goods that have a delicate structure, ones that rise quickly as carbon dioxide is produced.

Is Baking Bread A Chemical Or Physical Change Bread Poster
In essence, the rise of bread is a result of the chemical reaction of fermentation and the physical expansion of gases and steam. Both chemistry and physics are essential components of this delightful process. Takeaway. In conclusion, the physical and chemical components of baking bread combine to produce an intriguing process.

Case Based MCQ Sanjana while preparing cake used Science Class 10
The Organic Chemistry of Baking Bread. The chemistry that underlies the browning of bread. meats, etc. was first defined in 1912 by Louis-Camille Maillard and involves the polymerization of sugars and proteins. While this reaction is obviously messy (i.e. has many different pathways), the dominant chemical mechanisms were identified in a.

Is Baking Bread a Chemical Change? Baking Wit Oven Adventures
These reactions occur most rapidly under conditions of low moisture and at temperatures above about 130°C. Hence, they tend to kick in when we fry, bake, grill or roast.

PDF purpose of leavening agents in baking PDF Télécharger Download
In a large bowl, combine flour, cornmeal, sugar, salt and baking powder. Stir in egg, milk and vegetable oil until well combined. Pour batter into prepared pan. Bake in preheated oven for 20 to 25 minutes, or until a toothpick inserted into the center of the loaf comes out clean.

Chemical reactions in baking a cake Cake Baking
Baking bread is both a physical and chemical change. 1 It involves physical transformations such as the rise and browning of the dough due to heat, as well as chemical reactions like the fermentation of yeast and the Maillard reaction that contribute to the development of flavor, texture, and color in the bread. 2 3 4.

Baked bread containing assortment, bake, and bakery Food, Bakery
imidazoles. 'chocolate, bitter, nutty'. The molecules can also form polymers and precipitates. This page titled 1.12: Bread is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kate Graham. Bread is a staple food in many cultures. The key ingredients are a grain starch, water, and a leavening agent.

The Best Garlic Bread You'll Ever Eat Ambitious Kitchen
These enzymes are called amylases. Bread needs a rising or "leavening" agent. While some breads and cakes use baking soda to produce the gas for this, in our breads, yeast is used to ferment the sugar that has been released during fermentation. In doing so it releases carbon dioxide gas which is what makes the bread rise, and the sugar is.

Ultimate Troubleshooting Guide for Baking Bread
In bread making (or special yeasted cakes), the yeast organisms expel carbon dioxide as they feed off of sugars. As the dough rises and proofs, carbon dioxide is formed; this is why the dough volume increases. The carbon dioxide expands and moves as the bread dough warms and bakes in the oven. The bread rises and sets.

All three major stages of artisan bread baking. YouTube Artisan
Caramelization, which occurs at 356 degrees Fahrenheit, is the last chemical reaction to occur during the baking process. The reaction occurs when high heat causes sugar molecules to break down and release water, which turns into steam. Diacetyl, which gives caramel its butterscotch flavor, is produced during the first stages of caramelization.

The Science of Baking Soda
At its most basic level, the Maillard reaction is quite simple. When our food is heated to a temperature of at least 280°F, a chemical reaction occurs between amino acids (proteins) and carbohydrates (sugars) that causes it to brown. So essentially: protein + sugar + heat = browning.

Why Baking Bread A Chemical Change [Explained!] CUISINEIN
The ancient tradition of bread baking depends on a cascade of chemical reactions. As scientists have unravelled this complex chemistry, they have also found myriad ways to modify the process, say Bryan Reuben and Tom Coultate In short A series of chemical reactions take place throughout the process of turning flour into bread

Is Baking Bread a Chemical Change? Baking Wit Oven Adventures
The Maillard Reaction. The Maillard reaction is the chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives baked goods their characteristic color and flavor. This reaction begins at around 140°C (284°F) and is responsible for the golden brown color and savory flavor of crusts, crusts, and other baked goods.

Baking Soda vs Baking Powder What's the Difference? Baking soda
The process of making bread can be broken down at a very simple level into four steps. First, the ingredients are mixed; the four basic ingredients used to make bread are flour, water, yeast, and salt. Combining these creates a dough, which is then kneaded before being left to rise, before being baked.